Roof decking is an essential structural component that creates a firm foundation for roofing materials to ensure their durability and support. Roof decking or roof sheathing is usually in plywood or OSB and further designed to take additional loads such as those from snow, wind, or rooftop installation while maintaining the integrity of the roof.
Different Types of Roof Decking

The types of roof decks used are plywood, oriented strand board (OSB), tongue-and-groove wood, and steel decking. With a wide range of durability, weight, and moisture resistance, all those materials affect in turn the structural stability and long life expectancy required under weather and roof considerations.
-
Plywood Roof Decking
Plywood roof decking is formed from many thin sheets of wood glued together to give a strong yet stable surface. They are installed over joists in large sheets, ranging from ⅜”-to-¾” thick, depending upon rafter span. This capacity makes this roof decking good in terms of strength and longevity, thereby making it a fairly reliable option for most buildings.
-
Oriented Strand Board (OSB)
OSB roof deck is an engineered wood panel made up of wood strands compressed and glued together making sure structural stability, this most cost-effective wood substitute to plywood, source strength and moisture resistance based on the grade used. Most builders prefer OSB for roof decking in affordable pricing and functional performance in roofs.
-
Metal Roof Decking
Metal roof decking is made of steel or aluminium and, for enhanced strength and support, has a ribbed profile. Base layer for different roofing membranes is provided by the metal roof deck itself ensuring that it is remarkably long-lasting across different applications. Metal roof decking is available in many profiles and is normally adopted because of its durability against fire and other structural advantages.
-
Concrete Roof Decking
Concrete roof decking is a heavy, fire-resistant type mainly for commercial buildings. It provides thermal insulation and can be reinforced with either steel bars or mesh. Due to this heavy weight, it requires additional structural support. This type of roof decking is long term and durable, providing outstanding protection from environmental, external elements.
-
Wood Plank Decking
Wood plank decking comprises long wooden planks lined next to one another on rafters to form a stable roof deck. This being a traditional method usually with tongue-and-groove joints provides good tightness and is hence stronger. Roof decking with wooden planks is nowadays not very common, though in some applications it might still be preferred for aesthetic resultant.
Causes of Roof Decking Rot
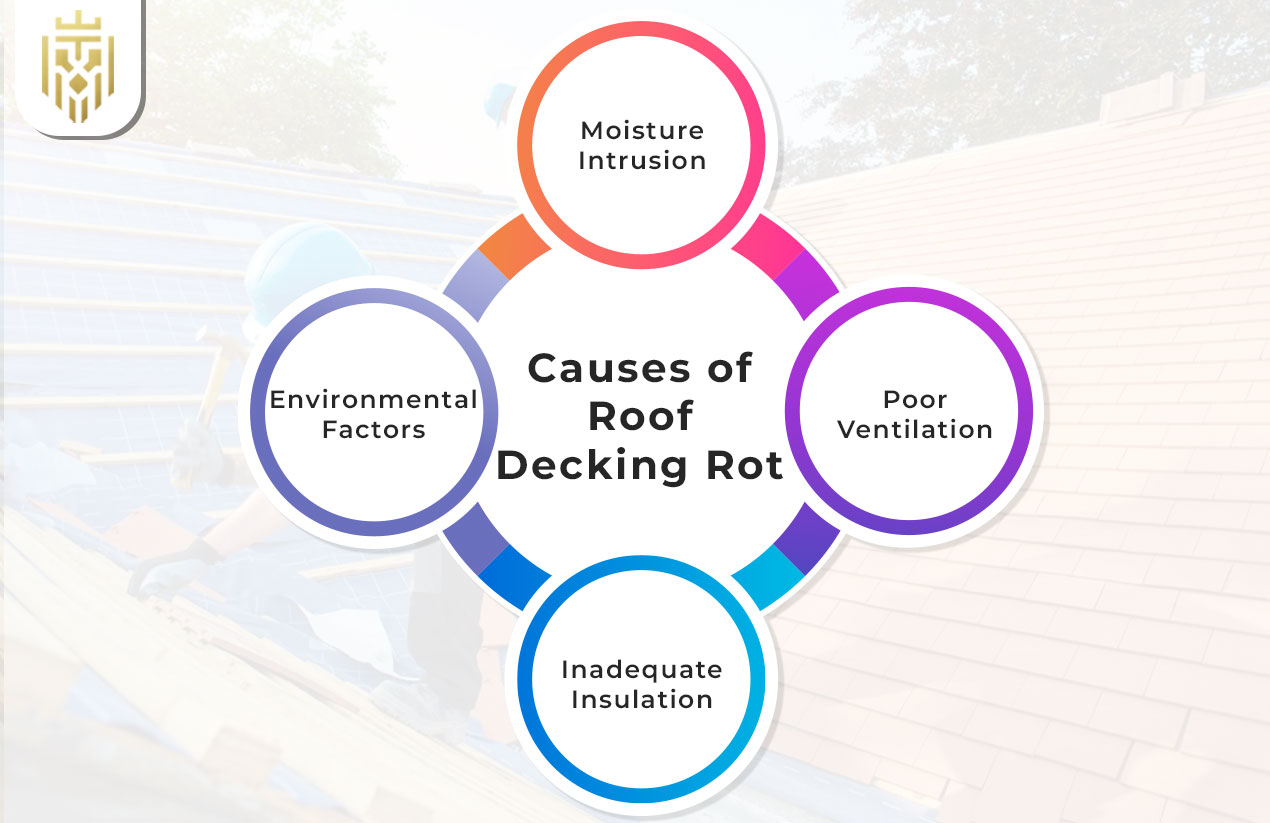
Roof deck decay takes place because of moisture accumulation, insufficient ventilation, leaking, or prolonged exposure to humid conditions. Roof behaviour is further worsened with disintegration of shingles, improper drainage, and trapping of condensation, adversely affecting the roof’s structural integrity and leading to costly repairs or replacements.
-
Moisture Intrusion
Roof decking rot occurs when moisture gets into the roof decking through leaks, clogged gutters, or poor installation. Slowly but surely, such lake water accumulates until it weakens the roof sheathing; therefore, this eventually results in some structural deterioration. It is also a good preventative measure against moisture intrusion in roof decking, by regularly performing maintenance to prolong its lifespan and avoid future costly repairs.
-
Poor Ventilation
Without proper ventilation, condensation builds up on the roof deck resulting in accelerated decay. This moisture traps mold growth, weakening roof decking and reducing its lifespan. To prevent this occurrence, proper airflow should be ensured to avert excess humidity from these roof sheaths for continued protection.
-
Inadequate Insulation
Poor insulation allows condensation along the temperature differentials, causing the roof deck to get soaked. This moisture-in persistence encourages rotting within the roof deck, thus hampering its structural integrity. Rooftop sheathing needs proper insulation for rot prevention and thus gives durability to roof sheathing.
-
Environmental Factors
Humidity, leaks, and temperature changes lead to the gradual deterioration of roof decking over time. Moist conditions for a long time will promote fungi growth and such conditions to hasten roof deck decay. Effective ventilation and timely maintenance can help protect the roof deck from adverse environmental conditions.
How Often Should Roof Sheathing Be Replaced?
Roof sheathing should generally get replaced every 20 to 30 years, according to the grade of material and exposure to the weather. Leaks, sagging, cracks, and rot are indicators that immediate action is needed to prevent further damage from occurring. Regular inspection assures that the roof decking remains structurally sound and can support the roofing system’s needs effectively.
FAQs
1) What is roof decking?
Roof decking is an essential structural component that creates a firm foundation for roofing materials to ensure their durability and support. Roof decking or roof sheathing is usually in plywood or OSB and further designed to take additional loads such as those from snow, wind, or rooftop installation while maintaining the integrity of the roof.
2) What is the best roof decking material?
Plywood and OSB remain the predominant types of materials used for roof decking, owing to its strength, low cost, and ease of installation. While metal decking offers great durability, composite materials have excellent moisture resistance properties that work well in damp climates.
3) What are the different types of roof decks?
The types of roof decks used are plywood, oriented strand board (OSB), tongue-and-groove wood, and steel decking. With a wide range of durability, weight, and moisture resistance, all those materials affect in turn the structural stability and long life expectancy required under weather and roof considerations.
4) What causes roof rot?
Roof deck decay takes place because of moisture accumulation, insufficient ventilation, leaking, or prolonged exposure to humid conditions. Roof behaviour is further worsened with disintegration of shingles, improper drainage, and trapping of condensation, adversely affecting the roof’s structural integrity and leading to costly repairs or replacements.









